Transaction (CRUD) Documentation
CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations are fundamental to effective data management in any system. They empower you to create, retrieve/read, update, and delete data, providing the essential building blocks for handling information within your application.
Introduction to Django CRUD Operations
-
What is CRUD and Why Do We Need It?
In the world of data management, CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) are like the ABCs for efficiently handling information. This section explores what CRUD is all about and why it's so essential in making applications work smoothly.
-
What is Database?
A database is a digital storage space for your application's data, like user information or product details. It's an organized and efficient way to keep and handle data, allowing your app to access, update, and utilize information easily.
Info: Sneat use Django's built-in SQLite database. SQLite is a lightweight database that comes bundled with Django, making it a fantastic choice for smaller projects and applications due to its simplicity and ease of use. If you decide to opt for a different database, you can consult the Django documentation, which offers guidance on selecting the most suitable databases for your Django project. -
Setting Up CRUD Database
Tip: This show basic example how Sneat database created.Creating a database table in Django is straightforward. Follow these steps with example code:
-
Create a Django Project: Create a Django project using the following command:
django-admin startproject test -
Create a Model: Define a model in a Django app's models.py file. A model represents the structure of your table. For example:
# models.py from django.db import models class Item(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=100) description = models.TextField() price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2) -
Admin Interface (Optional): To manage your data easily, update the admin.py file. This will register and make your data visible in Django admin:
# admin.py from django.contrib import admin from .models import Item admin.site.register(Item) -
Migrations: Create migration files for your model. Run the following commands:
python manage.py makemigrations python manage.py migrate -
View: Create a view to display your data. For example:
Info: Sneat use Class based View. For more information about Class based View, refer to this documentation. The Sneat transaction app also provides insights into enhancing the get_context_data method to retrieve data from the database.# views.py from django.shortcuts import render from .models import Item from django.views.generic import TemplateView class ItemListView(TemaplateView): def get_context_data(self, **kwargs): context = super().get_context_data(**kwargs) context["items"] = Item.objects.all() return context
-
Transaction Management App
-
Folder structure
apps └── 📂 transactions ├── 📂 transaction_list │ └── 📄 views.py > Contain view for displaying Transaction Table. ├── 📂 transaction_delete │ └── 📄 views.py > Contain view for deleting Transaction. ├── 📂 transaction_add │ └── 📄 views.py > Contain view for adding Transaction. ├── 📂 transaction_update │ └── 📄 views.py > Contain view for update Transaction. ├── 📄 urls.py > Url for Transaction app. ├── 📄 models.py > Contain Profile Model. ├── 📄 forms.py > Contain Form to take Model. └── 📂 templates ├── 📄 transactions_add.html ├── 📄 transactions_list.html └── 📄 transactions_update.html -
Transaction List
This page displays data from the database using the Datatable library. Additionally, it features widgets that provide key statistics, including the total number of transactions, total paid amount, total due amount, and total canceled transactions.
Info: This page will look different based on user permissions. For example, if a user doesn't have permission to delete transactions, the delete button will not be visible. For better understanding please refer Permissions and AuthorizationAdmin transaction app
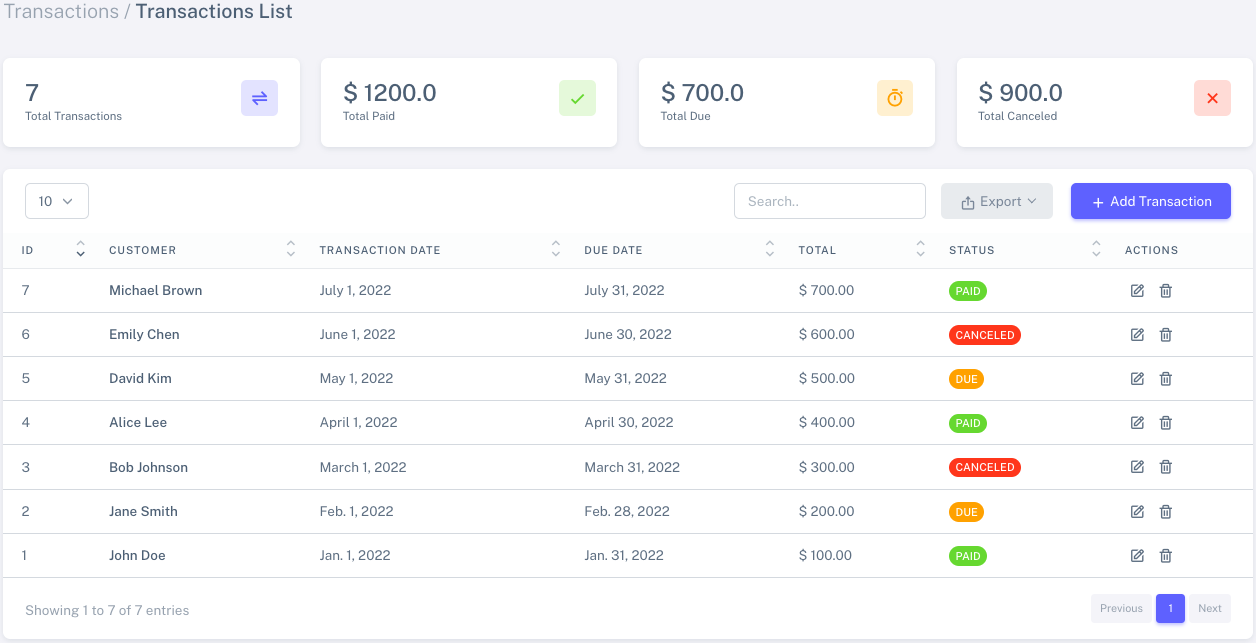
Client transaction app
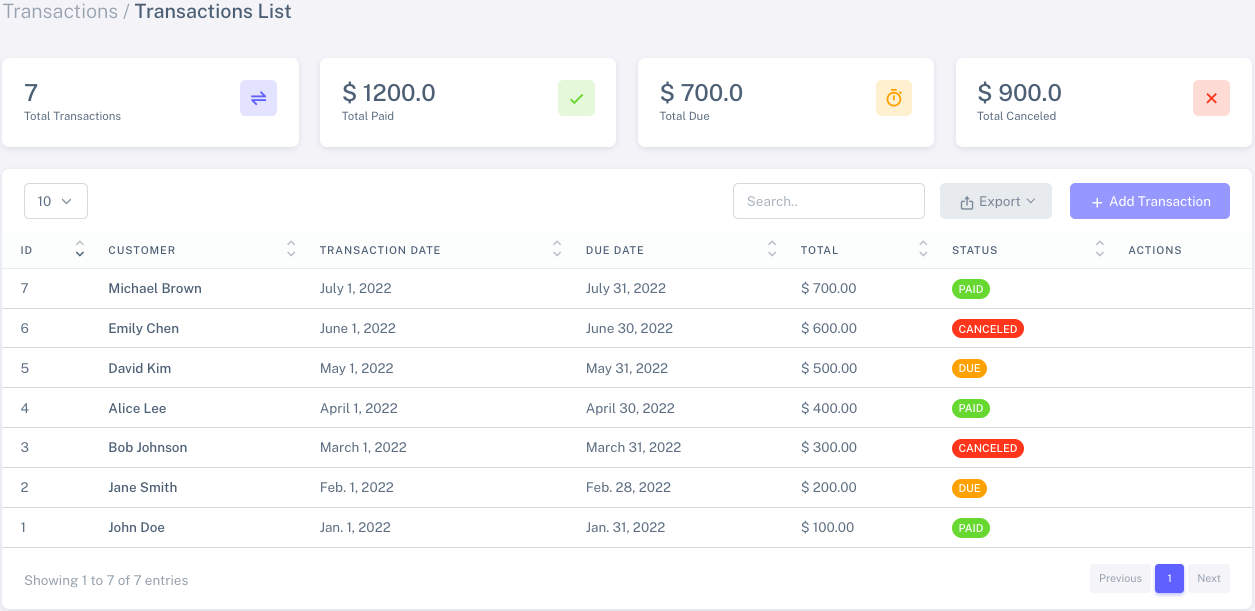
-
Transaction Add
The transaction add page allows users to input new transactions into the database. It includes a form to gather Customer name, transaction date, due date, transaction amount, and transaction status. The page has both client-side validation to provide instant feedback on data input errors and server-side validation. When valid data is entered, the form submits the information to the database, and users are notified with a toast. In case of errors, error messages are displayed.
The date input filed use select2 library
ImplementationThe 'transaction add' view, located in
transactions/transaction_add/views.py, is implemented as a class-based view. It employs the permission_required decorator to restrict access, ensuring only users with the necessary permissions can use this view, as shown in the image above.-
We've made updates to enhance its functionality:
-
The
get_context_datamethod retrieves variables from the view and passes them to the template. - The
postmethod handles data submission to the database and validation."
-
The
-
Transaction Update
The transaction update page allows users to update existing transactions in the database.
ImplementationThe 'transaction update' view, located in
transactions/transaction_update/views.py, is a class-based view designed for simplicity. It serves the straightforward purpose of retrieving an existing transaction and pre-filling the input fields with its data. Users can make changes to the input fields, and upon form submission, the view seamlessly updates the transaction in the database. -
Transaction Delete
The delete option is present in two place in transaction list where all the all data is shown and in transaction update where user can delete the transaction. In Sneat this option is only available for admin user or user with required permission.
The delete button has been seamlessly integrated with SweetAlert2 to enhance the user interface (UI) experience. You can locate the integration details in the
transactions-delete.jsfile. For more information on SweetAlert2's functionality and instructions on updating the SweetAlert, please refer to the documentation.Implementation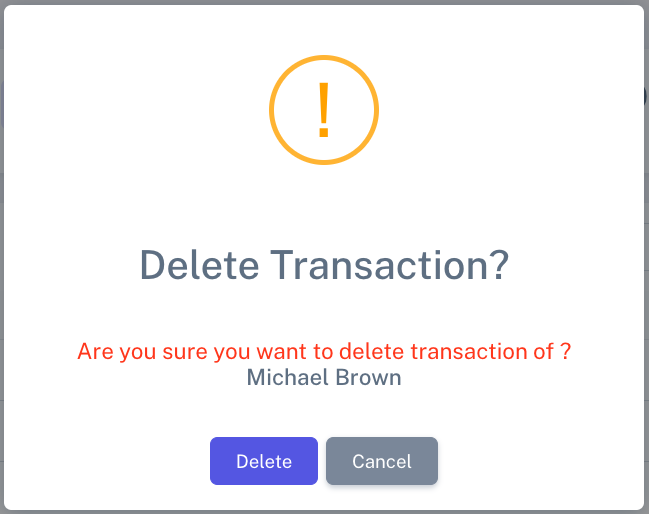
The 'transaction delete' view, residing in
transactions/transaction_delete/views.py, is a class-based view thoughtfully designed for simplicity. Leveraging Django's user-friendly framework, it harnesses built-in functionality for data deletion. This view simply requires an 'id' parameter and seamlessly removes the corresponding data from the database.# views.py from django.views.generic import DeleteView class ItemListView(DeleteView): def get(self, request, pk): item = Item.objects.get(id=pk) item.delete() return redirect("transaction_list")